Plastic extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. At Primo, we have been extruding plastic profiles since 1959. Both extruders and the process itself have undergone significant progress over the years.
Industrial extrusion at its core
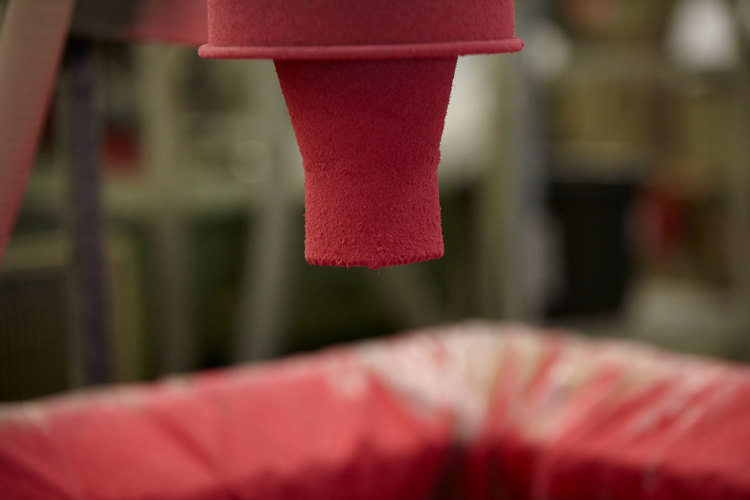
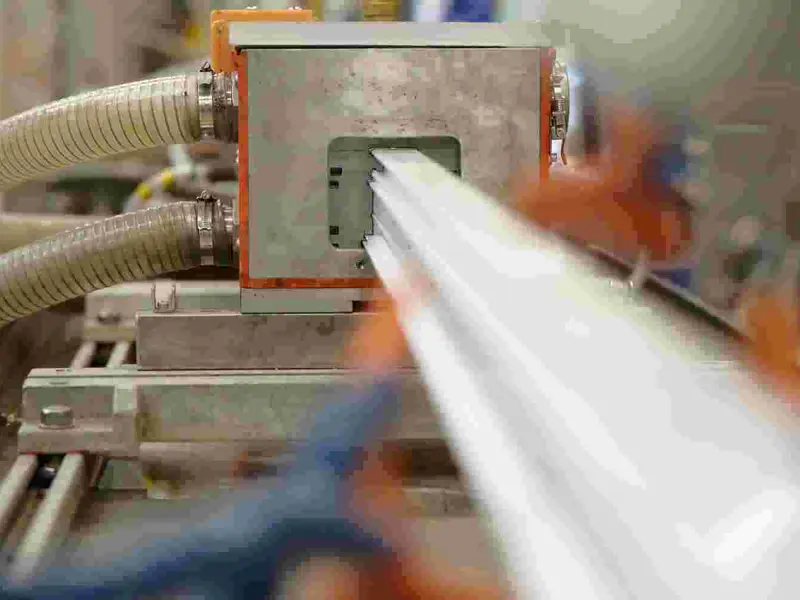
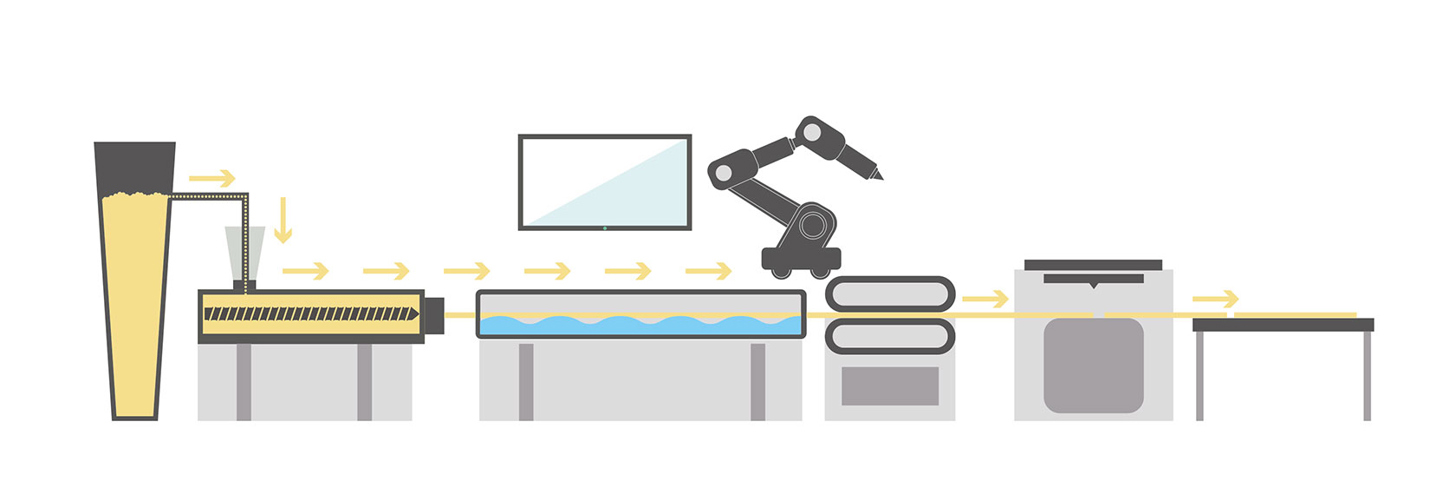
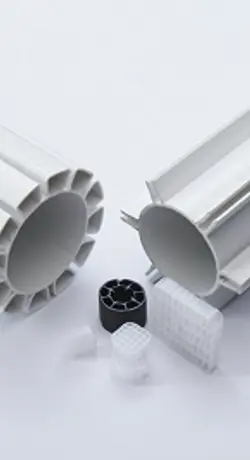
The plastic extrusion process can be broadly described as melting plastic pellets or powders and forcing them through a special die to form continuous shapes such as pipes, seals, tubes, gaskets or other custom profiles designed to fit a specific end product.
Plastic is only one of the raw materials used in industrial extrusion. Other materials commonly used in industrial extrusion include metal, ceramics and food. For example, the technique is widely used in the food industry, where products such as minced meat, pasta and even cheese puffs are produced by extrusion.
Industrial extrusion is a manufacturing process used to create components by forcing material through a shaped die. The material is pushed or pulled through the die, forming long, continuous shapes that are then cut to the desired length. This process is mainly used to produce large quantities of uniform products.
A specialised production setup
Today, advanced technology and digital monitoring ensure high-quality and cost-saving processes for the benefit of a wide range of industries and numerous applications at our highly efficient and automated production plants in Europe and in China.
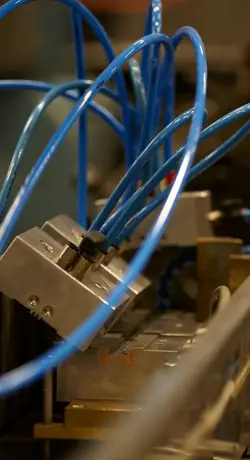
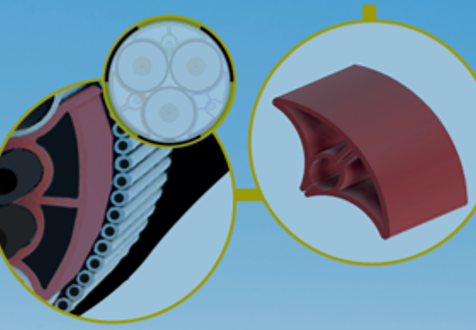
In plastic extrusion, the heated plastic mass is put under pressure by a screw and is pressed through a die (the tool). The profile is then cooled down and hardens into its final solid state. This way, a profile can be produced in any length, which is an advantage, for example, when producing parts for cables that are rolled directly onto cable reels.
Extruded plastic profiles for all kinds of purposes
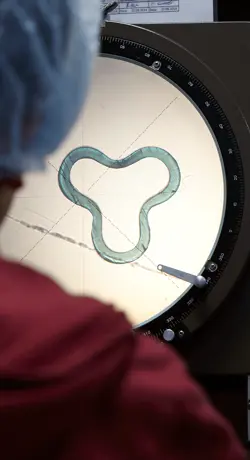
The extrusion of plastic profiles allows for a wide range of custom extruded profiles with unique designs and properties. In plastic profile extrusion, the design and development of the tooling is a critical phase that defines the properties of the extruded plastic profile. It could be a lightweight window profile with excellent insulating properties due to its air chambers, a low tolerance tube for medical devices or a shaped filler for offshore power cables. The applications are endless. Primo specialises in developing custom extruded profiles in close cooperation with our customers.